Running a startup can be hard. From growing the team to raising money, acquiring customers, and managing a budget, there are likely hundreds of fires burning at all times.
To help manage these fires (and extinguish some), we’ve compiled a list of the 5 key metrics that every startup should know, along with tips on how to measure them. We'll also explore how your business model can affect the way you view your data metrics. Alright, let’s jump in!
What are data metrics and why are they useful?
Data metrics are points of information that give you an idea of how your business is doing. Revenue, for instance, is a basic metric that every business should know. It tells you how much you're earning, which is crucial to measuring your success.
You might also know data metrics by another name: KPIs. KPIs, or key performance indicators, refer to metrics that give you an idea of how well your business is performing.
Data metrics are essential to businesses in the same way that a compass is essential to travel. They tell you where you are and help you know if you're going where you intend to. They can serve as a warning sign or a signal to keep going.
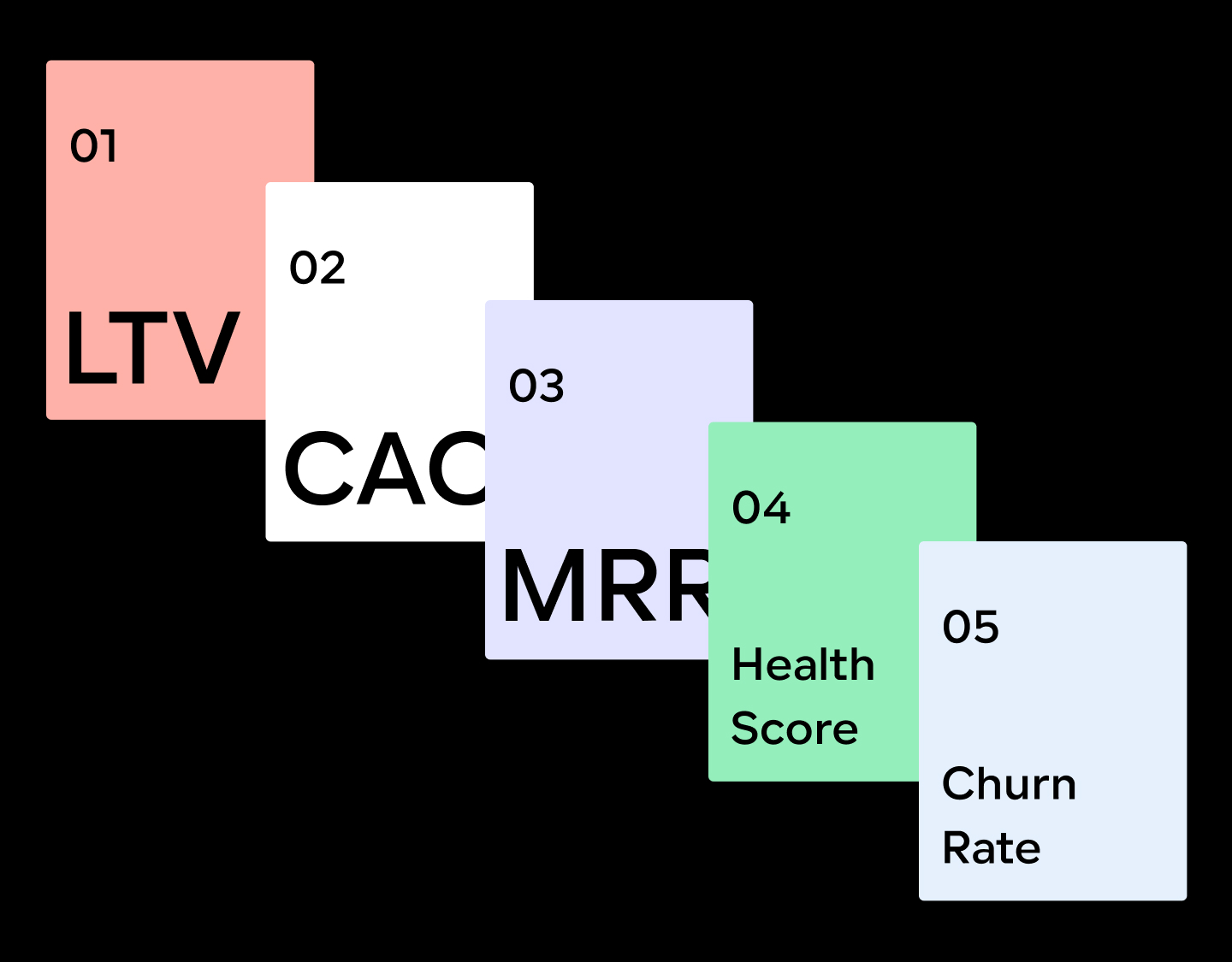
5 data metrics for startups
There are nearly infinite metrics you could track at any given time. Most of them, however, are not true KPIs and won’t provide meaningful insight into your startup’s performance. Below are five metrics that will give you the knowledge you're looking for.
1. LTV
The first data metric is one of the staple customer insights: LTV (Lifetime Value). LTV gives you an idea of the net earnings a customer will bring to your business over the course of their patronage.
For example, if your average customer spends $50 and never returns, then your LTV is $50. On the other hand, if you're a subscription service with customers who stick around for months, calculating LTV becomes more complex.
The usual method of calculating LTV is to subtract the customer acquisition cost (CAC) from the total revenue a customer brings. Do this for tens or hundreds of customers, depending on your business scale, and calculate an average. There are other methods, but this is generally the way to go.
2. CAC
Speaking of customer acquisition cost, that's the second metric we recommend tracking: CAC. True to its name, CAC estimates how much you spend to acquire a customer.
This can be a difficult metric to calculate since spending is usually spread across various marketing campaigns and channels, targeting different demographics, and sometimes even influenced by word of mouth.
Still, CAC is vital. It's used to calculate other metrics and tells you whether you're truly earning a profit. If you spend $100 acquiring a customer and they only spend $50, you need to know that!
To calculate CAC, track the number of customers acquired over a specific period alongside your marketing spending. Divide your total marketing spend by the number of customers acquired during that period to determine the cost per customer.
3. MRR
Third on the list is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue). MRR provides insight into the revenue you're generating every month. This metric is typically used to gauge the performance of SaaS and subscription-based businesses, though it can be valuable in other sectors as well.
MRR is particularly important because it is predictive. Knowing your monthly revenue helps you estimate future earnings, which is key for subscription-based businesses with high upfront costs.
4. Health Score
One of the most important customer insights is your customer health score. A health score measures a customer’s engagement and likelihood to churn. Customers with high scores are your most loyal, while those with low scores are your least engaged.
Health scores are among the best ways to improve customer retention. Retaining a customer is generally more cost-effective than acquiring a new one. By using health scores, you can hold on to loyal customers and intervene before disengaged customers churn.
Calculating a health score can be challenging because the data used may vary from one business to another. Some companies use participation in loyalty programs and community engagement, while others focus solely on repeat sales. The key is having the right data to generate an effective health score.
5. Churn Rate
The final metric to track is churn rate—the percentage of customers leaving your business over a given time.
To calculate churn rate, determine the number of customers at the beginning of a period (typically one month) and at the end of that period. Subtract the end number from the beginning number, then divide the difference by the initial number of customers. For example, if you start with 100 customers and end with 90, your churn rate for that month is 10%.
While it's standard to measure churn monthly, some companies opt for quarterly periods (90 days) to avoid counting inactive customers as churned. Although churn is inevitable (you’ll never retain 100% of your customers), data metrics like health scores can help reduce customer attrition. This is one of the key reasons that data is crucial to your startup's success.
How your business model affects your metrics
Now that we've covered the various customer data insights your startup should track, let's briefly touch on a few nuanced points. Although these metrics are valuable to all businesses, your business model can and should affect how you use your data.
How eCommerce businesses can use metrics
eCommerce businesses are largely B2C and operate by selling goods directly to customers. In this context, the most important metrics to leverage are LTV, CAC, and MRR. These metrics can help streamline your marketing efforts and ensure you don't overextend your budget.
 In ecommerce, customer experience is everything. Find 5 methods to bring data-led growth into your business strategy in our Data-Led Growth in Ecommerce Ebook →.
In ecommerce, customer experience is everything. Find 5 methods to bring data-led growth into your business strategy in our Data-Led Growth in Ecommerce Ebook →.
Using data metrics as an enterprise startup
For enterprise providers or B2B businesses, the goal is to land and retain large clients as often and as long as possible. This means closely monitoring customer health scores, churn rate, LTV, and CAC.
Data metrics for SaaS and subscription services
Lastly, SaaS and subscription-based businesses—which have boomed over the last ten years—should focus on MRR, churn rate, and health scores. Monitoring these metrics will help you maximize the value of each customer and project future revenue.
Access and activate your customer data insights with Weld
Now that you know which customer data insights your startup should be tracking, it's time to put that data to work. Reach out to the team at Weld today and learn how you can make the most of your data.