Looking for the best ETL tool in 2026? This guide compares 40 ETL and ELT tools by connectors, pricing model, reliability, and use case—so you can pick the right platform for your stack.
Quick picks (2026):
- Best Unified ELT + reverse ETL: Weld
- Best open-source ELT: Airbyte
- Best fully managed enterprise ELT: Fivetran
- Best streaming / CDC-first: Estuary
- Best visual ELT for cloud warehouses: Matillion
Jump to: Comparison table · Full tool list · FAQs
Top 40 ETL Tools for 2026 (Compared by Features, Pricing & Use Cases)
Choosing an ETL tool in 2026 isn’t just about moving data, it’s about syncing teams, scaling infrastructure, and enabling fast decisions. Whether you're building pipelines as a data engineer or looking to streamline reporting as an analyst, the ETL space is full of great tools, each with their own strengths.
What is ETL? A Simple Guide to Extract, Transform, Load
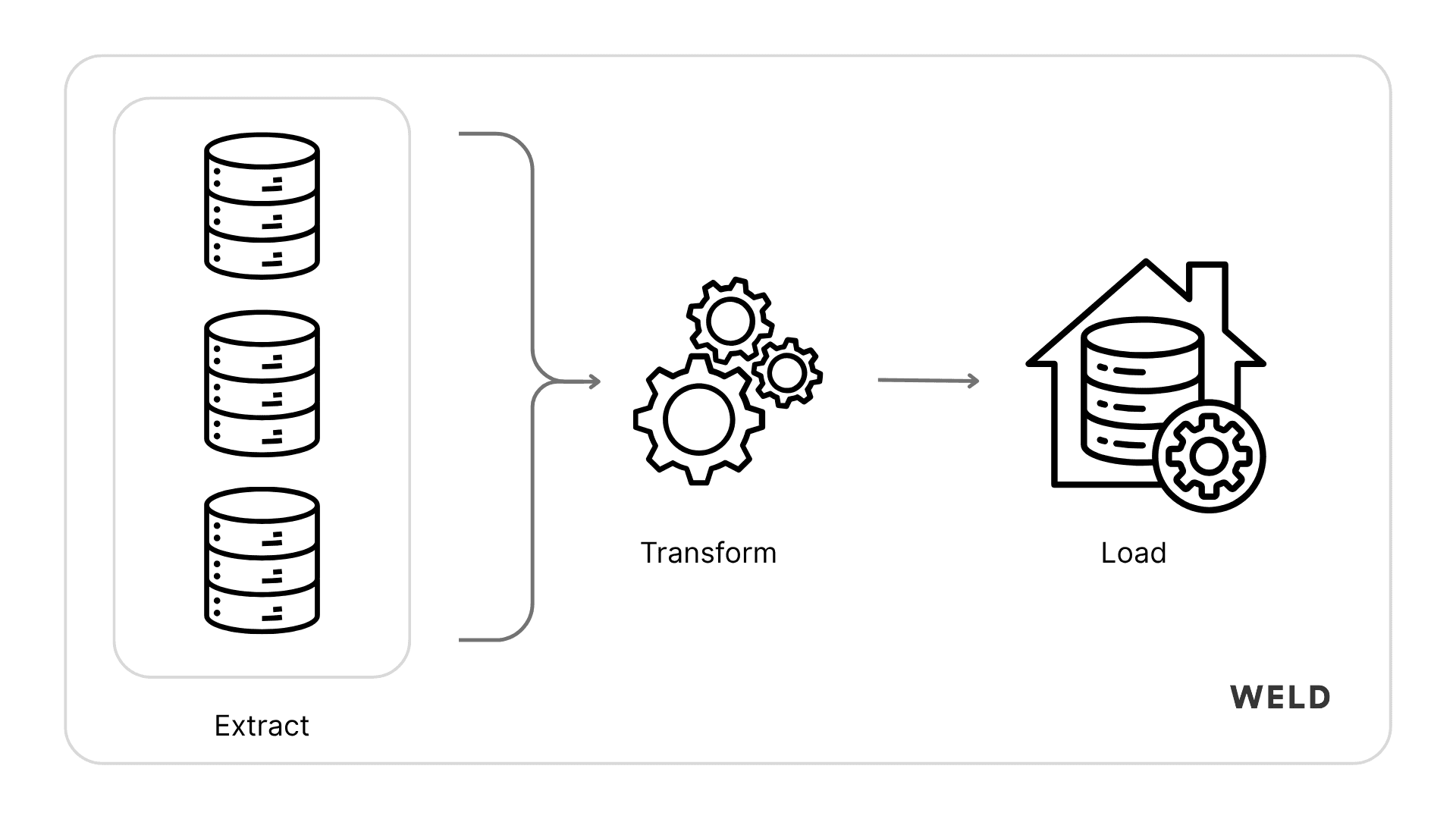
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load, a core data process used to bring together information from different systems and make it usable for reporting, analysis, and automation. It’s a foundation of modern data infrastructure and one of the most important building blocks for any business working with data.
Here’s how it works:
- Extract: First, data is pulled (or extracted) from various source systems. These can be anything from marketing platforms like HubSpot or Meta Ads to e-commerce tools like Shopify or Stripe. At this stage, the data is often messy, siloed, and structured in different ways depending on the tool.
- Transform: Once the raw data is extracted, it needs to be cleaned, restructured, and transformed. This could mean joining tables, renaming columns, fixing data types, or calculating new fields. The goal is to turn inconsistent data into something usable and trustworthy, often using tools like SQL or visual transformation layers.
- Load: Finally, the transformed data is loaded into a centralized data warehouse, such as Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift. Once it’s there, it becomes a single source of truth that teams can use for dashboards, reports, or powering automations.
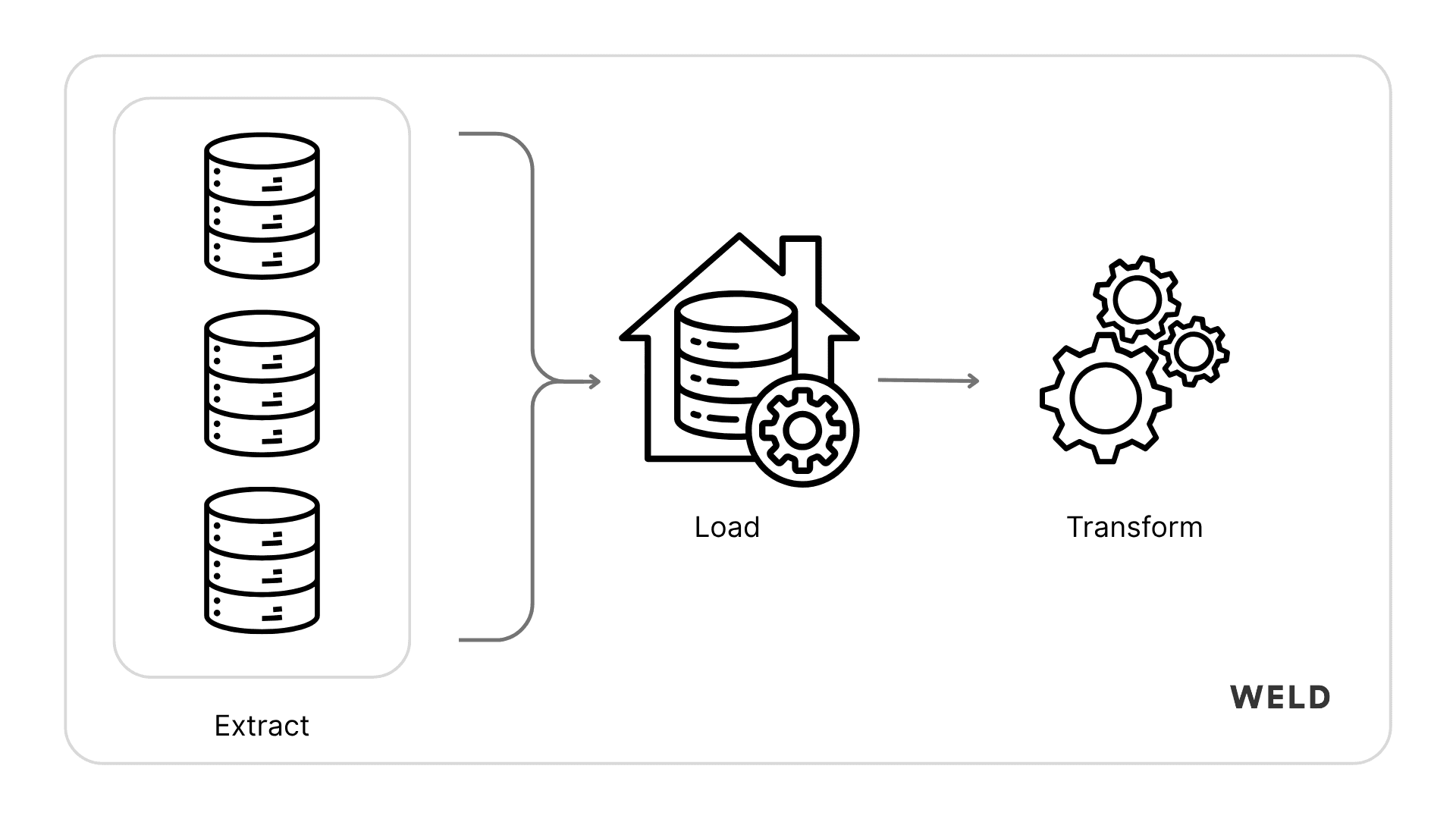
Another version of this process is often called ELT, which flips the last two steps, bringing raw data into the warehouse first, then doing all the transformations inside the warehouse itself. This approach is common with today’s cloud-native tools because it’s faster, more flexible, and easier to scale.
Many companies also go a step further by enabling reverse ETL, which sends data back from the warehouse into everyday business tools. This means sales teams can see enriched customer data in their CRM, marketing teams can create better segments, and finance teams can automate reporting, all using the same trusted data.
In short, ETL helps you go from raw, scattered information to reliable, actionable insights. And the right ETL tool can save hours of manual work, reduce errors, and enable better decisions across the business.
Below you'll find a complete list of the top ETL tools in 2026, along with pros, cons, fresh reviews, and a final comparison to help you choose the right one.
What should you consider when choosing an ETL tool?
When evaluating ETL tools, there are several key factors to consider:
- Connectors and data sources: Look for tools that support the data sources and destinations you use.
- Ease of Use: Consider the user interface and how easy it is to set up and manage pipelines. Some tools are more developer-focused, while others offer no-code or low-code options.
- Transformation and Capabilities: Evaluate how the tool handles data transformations. Does it support SQL, visual transformations, or custom code? Make sure it fits your team's skill set.
- Scalability: Ensure the tool can handle your current data volume and scale as your business grows. Look for features like auto-scaling and performance optimization.
- Pricing: Understand the pricing model and how it aligns with your budget. Some tools charge based on data volume, number of connectors, or users.
Try to take advantage of free trials or demos to get a hands-on feel for the tool before committing.
How we evaluated these ETL tools (2026)
We compared tools based on: connector coverage, warehouse support, transformation options (ETL vs ELT), reliability in production (monitoring, retries, schema drift), security/compliance, and pricing model.
ETL Tool Comparison Table (2026)
| Tool | Website | Type | Deploy | Pricing model | Build | Transform | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weld | weld.app | ETL/ELT + Reverse ETL + CDC | SaaS | Subscription | UI | Yes | all-in-one production ETL — fast to deploy & reverse-ETL capable |
| Airbyte | airbyte.com | ELT | SaaS + Self | Usage (cloud) / Free (self) | UI + Code | Limited | flexible OSS connectors — self-host & customizable |
| Fivetran | fivetran.com | ELT + Reverse ETL + CDC | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Limited | low-maintenance enterprise — reliable at scale |
| Hevo Data | hevodata.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Subscription | UI | Yes | quick setup, no-code loads — analyst-friendly |
| Estuary | estuary.dev | ELT + CDC (streaming) | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Limited | low-latency streaming/CDC — real-time pipelines |
| Matillion | matillion.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Yes | warehouse transformations — visual ELT for analysts |
| Keboola | keboola.com | ETL/ELT + Reverse ETL | SaaS + Hybrid | Usage/Quote | UI + Code | Yes | governed enterprise flows — governance & orchestration |
| Qlik Talend Cloud | talend.com | ETL/ELT + CDC | SaaS + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | enterprise governance — data quality & trust features |
| Meltano | meltano.com | ELT | Self | Free + paid support | Code | No | dev-first CI/CD pipelines — code-centric workflows |
| Rivery | rivery.io | ELT + Reverse ETL | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Yes | UI-driven ELT & activation — low-code activation workflows |
| Azure Data Factory | azure.microsoft.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Yes | Azure-native integration — great for Azure stacks |
| AWS Glue | aws.amazon.com/glue | ETL | SaaS | Usage-based | Code | Yes | serverless Spark ETL — AWS-native scalable ETL |
| Skyvia | skyvia.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Tiered | UI | Limited | small teams & ad-hoc loads — quick scheduled imports |
| Portable.io | portable.io | EL | SaaS | Per-connector | UI | No | long-tail/niche connectors — great for niche APIs |
| Integrate.io | integrate.io | ETL/ELT + Reverse ETL | SaaS + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | low-code enterprise ETL — hybrid deployments supported |
| Dataddo | dataddo.com | ETL/ELT + Reverse ETL | SaaS | Subscription | UI | Limited | marketing & analytics loads — analyst-focused connectors |
| dltHub (dlt) | dlthub.com | ELT | Self | Free | Code | No | Python-first ingestion — code-first pipelines |
| Informatica | informatica.com | ETL/ELT + Reverse ETL + CDC | SaaS + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | large-scale enterprise ETL — governance & data quality |
| CloverDX | cloverdx.com | ETL/ELT | Self + Hybrid | Quote | UI + Code | Yes | complex transformations — heavy-duty ETL & transformation engine |
| Microsoft SSIS | learn.microsoft.com | ETL | Self | License | UI | Yes | SQL Server-centric ETL — best for Microsoft stacks |
| IBM DataStage | ibm.com | ETL | Self + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | enterprise batch processing — high-throughput ETL workloads |
| Oracle Data Integrator | oracle.com | ELT | Self + Hybrid | License | UI + Code | Yes | Oracle-focused ELT — pushdown ELT for Oracle environments |
| SAP Data Services | sap.com | ETL | Self + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | SAP ecosystems — integrates with SAP platforms |
| Google Cloud Data Fusion | cloud.google.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Usage-based | UI | Yes | GCP-native pipelines — BigQuery integration & managed visual ETL |
| Stitch | stitchdata.com | EL | SaaS | Tiered | UI | No | simple ELT & quick loads — quick setup for small teams |
| Qlik Replicate | qlik.com | Replication + CDC | Self + Hybrid | Quote | UI | No | low-impact CDC replication — efficient change replication |
| Striim | striim.com | Streaming + CDC | SaaS + Self | Quote | UI + Code | Limited | real-time streaming ETL — enterprise streaming use-cases |
| SnapLogic | snaplogic.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Yes | enterprise integration hub — broad connectors & automation |
| Databricks Lakeflow | databricks.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Usage-based | UI + Code | Yes | Databricks-native flows — lakehouse-native pipelines |
| IBM StreamSets | ibm.com | ETL/Streaming | SaaS + Hybrid | Quote | UI | Limited | hybrid streaming pipelines — visual streaming & governance |
| Apache NiFi | nifi.apache.org | ETL/Dataflow | Self | Free | UI | Limited | flow-based data movement — routing, throttling, provenance |
| Apache Hop | hop.apache.org | ETL | Self | Free | UI | Yes | open-source ETL design — reusable pipeline components |
| Apache Kafka | kafka.apache.org | Event streaming (infra) | Self / Managed | Free | Code | N/A | streaming backbone — event streaming infrastructure |
| Debezium | debezium.io | CDC connector | Self | Free | Code | N/A | log-based change capture — CDC into Kafka |
| Singer | singer.io | ETL spec / taps & targets | Self | Free | Code | No | modular developer flows — composable taps & targets |
| Matia | matia.io | ELT | SaaS | Subscription | UI | Limited | simple analytics ingestion — fast analytics loads |
| Xplenty | xplenty.com | ETL/ELT | SaaS | Subscription | UI + Code | Yes | cloud visual ETL for teams — visual pipeline builder |
Top ETL & ELT Tools to Know in 2026
If you’re comparing ETL tools in 2026, the “best” option usually depends on your stack (warehouse vs hybrid), whether you need real-time, and how much engineering time you can afford.
How to choose an ETL / ELT tool
-
Do you need ETL or ELT?
- ELT = load to warehouse first, transform in-warehouse (common for Snowflake/BigQuery/Redshift).
- ETL = transform before loading (more common with legacy/on-prem or strict control needs).
-
Batch vs real-time:
If you need operational use cases (fraud, personalization, near-live dashboards), prioritize CDC + low-latency pipelines. -
Self-hosted vs managed:
Open-source gives control, but you own maintenance. Managed tools trade control for speed and reliability. -
Pricing model match:
Usage-based pricing can spike. If you want cost predictability, favor flat or clearly tiered plans. -
Transformations + orchestration:
Some tools are ingestion-only. Plan whether transformations live in dbt/warehouse vs inside the platform.
1. Weld

Weld is a modern ETL + reverse ETL platform designed to help teams move, transform, and activate data quickly. It combines connectors, orchestration, dbt support, and transformation tooling in one interface, making it easier to run a full data stack without managing infrastructure. Weld is best for teams that want fast implementation, predictable pricing, and production-grade pipelines.

Pros:
- Unified ETL + reverse ETL in one platform
- 300+ connectors for SaaS tools, databases, and ad platforms + custom connector features
- Real-time syncs (up to every minute) with support for change data capture (CDC)
- Predictable subscription pricing
- AI-powered transformation layer with full SQL support
- dbt integration, orchestration, and version control built in
- Enterprise-grade security: SSO, 2FA, audit logs, access tokens
- Multiple destinations and robust reverse ETL capabilities
- No infrastructure management required, fully cloud-hosted
Cons:
- Cloud-only (not self-hosted)
- Deeply custom ETL logic may still require engineering effort
- Focused on cloud data warehouses (less ideal for heavy hybrid/on-prem)
Pricing model: Subscription (starts at $99 / 5M active rows)
"Weld’s graphical interface is intuitive and easy to work with, even for teams with limited SQL experience. Its flexibility across sources—from databases to Google Sheets and APIs—made onboarding smooth, and performance across larger workloads was consistently strong. Support was responsive and helpful throughout our setup and ongoing use."
Reviews: 📝 G2 reviews
2. Airbyte

Airbyte is an open-source ELT data integration platform known for its large connector library and flexibility. It’s popular with modern data teams who want the option to self-host or use a managed cloud version. Airbyte is best for technical teams that want customization and are comfortable owning pipeline operations.

Pros:
- 550+ connectors
- Open-source + managed cloud version
- Capacity-based pricing (2025)
- Python SDK & low-code connector builder
Cons:
- Self-hosted version requires more maintenance
- More suited for advanced teams
- Connector quality can vary (open-source)
- High dependence on community
Pricing model: Credit-based usage (cloud) + free open-source (self-hosted)
Pricing: $2.50/credit (one million rows = 6 credits; 1 GB = 4 credits)
If you don't have workloads that currently use DBT or fit well into that model, this probably isn’t the tool for you.
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
3. Fivetran

Fivetran is a managed cloud ELT platform that automates ingestion from many sources into warehouses like BigQuery, Snowflake, and Redshift. It’s known for reliability, minimal setup, and “set-it-and-forget-it” operations. Fivetran is best for teams prioritizing low maintenance and connector stability.

Pros:
- Fully automated
- Schema drift handling
- Wide variety of connectors
- Robust security protocols
- Detailed and helpful documentation
- Near real-time replication capabilities
Cons:
- Complex and expensive pricing model
- Depends on external tools for transformations (e.g., dbt)
- Doesn't support transformations pre-load
- No AI assistant or advanced automation features
- Steep learning curve for dbt beginners
Pricing model: Usage-based (MAR)
Pricing: Usage-based, starting $500 for 1 million MARs (no fixed base)
Reviews: 📝 G2 reviews
4. Hevo Data

Hevo is a no-code ETL/ELT platform designed to automate ingestion into data warehouses with minimal engineering effort. It’s built for teams that want fast setup, monitoring, and simple pipeline management. Hevo is best for organizations that value ease of use and quick time-to-value.

Pros:
- Supports ETL and ELT
- Plenty of fully maintained connectors
- Great for non-technical users
- Simple UI that's easy to work with
- Affordable pricing
Cons:
- Limited features for advanced use cases
- Limited custom scheduling features
- Only 50 connectors available on the Free plan
- Less flexible for deeply customized pipelines
- Error messages and status codes could be better
Pricing model: Subscription
Pricing: Starts at $299 / 5M rows
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
5. Estuary

Estuary Flow is a real-time ETL/ELT and data integration platform for batch and streaming pipelines. It supports low-latency pipelines using change data capture (CDC), automated schema evolution, and connector-driven pipeline building. Estuary is best for teams that need real-time movement without running a full streaming stack themselves.
Pros:
- Real-time data sync
- Change Data Capture (CDC) support
- Easy UI for event workflows
- Automatic schema evolution with exactly-once delivery guarantees
- 100+ no-code connectors for databases, SaaS apps, and message queues
Cons:
- Smaller community
- Requires event-oriented thinking
- Connector catalog still growing; niche/new APIs may need custom work
- Premium pricing model can be expensive for small teams
Pricing model: Consumption-based + per-connector
Pricing: $0.50/GB consumed + per-connector fee
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
6. Matillion

Matillion is a cloud-first ETL/ELT tool designed for building pipelines and transformations in platforms like Snowflake, BigQuery, and Redshift. It offers a low-code interface with scheduling, monitoring, and orchestration features. Matillion is best for teams that want visual pipeline development with cloud data warehouses.

Pros:
- dbt integration
- Large number of connectors
- On premise options
- Has both ELT and ETL capabilities
Cons:
- Usage-based pricing can spike
- Higher learning curve for small teams
- Requires upfront investment and implementation
Pricing model: Credit-based usage
Pricing: $2.00 per credit
Built-in connectors to heaps of systems; ability to create custom connectors; active community and quick responses to forum questions
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
7. Segment

Segment (Twilio Segment) is a customer data platform focused on collecting and routing customer event data in real time. It’s commonly used to unify event streams across analytics, marketing, and CRM tools, often alongside a warehouse. Segment is best for customer event tracking and activation workflows.
Pros:
- Real-time data integration capabilities
- Pre-built and maintained connectors for popular data sources
- Advanced features for managing customer data
- Easy to setup and use
Cons:
- Quickly becomes very expensive
- Not suitable if you only need ELT ingestion
- Heavily skewed toward sales and marketing platforms
- Custom integration or customization can be hard
Pricing model: Tiered subscription (event/visitor-based)
Pricing: $120/month 10,000 visitors
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
8. Keboola

Keboola is a cloud platform for building and managing complete data pipelines with both code and no-code workflows. It combines connectors, orchestration, transformations, versioning, auditing, and cost monitoring. Keboola is best for teams that want a flexible end-to-end pipeline workspace.
Pros:
- Wide range of features
- Option to build custom components with API first approach
- Transformations that support both ELT and ETL
- Good academy to learn
Cons:
- Complex UI
- Orchestration features are lacking
- Credit consumption pricing can become expensive
- Smaller user base
Pricing model: Custom / usage-based
Pricing: Custom pricing
What I like most is that Keboola is a very simple tool, allowing even a single person to manage the data pipelines of a large company."
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
9. Qlik Talend (Qlik Talend Cloud)
Qlik Talend Cloud is Qlik’s enterprise ETL and ELT data integration platform (following Qlik’s acquisition of Talend in 2023). It combines data replication, change data capture (CDC), data pipelines, and (by tier) data quality and governance in a single suite for cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
If you’re looking for an ETL tool that can support real-time data pipelines and modern lake or lakehouse architectures while maintaining strong governance, Qlik Talend is a strong option—especially for mature data teams that need both breadth (many sources and targets) and depth (CDC, transformation, and data trust capabilities).

Pros:
- Enterprise-grade ETL + ELT (advanced transformation in higher tiers)
- Strong replication + CDC support for near real-time pipelines
- Built for hybrid and multi-cloud data movement (warehouse, lake, lakehouse)
- Large and continuously expanding connector ecosystem
- Enterprise tier support for complex sources like SAP and mainframe
- Premium/Enterprise tiers add broader capabilities beyond ETL, including API integration, data quality, and governance features
Cons:
- Best suited to experienced data teams (platform breadth increases implementation complexity)
- Can be expensive for smaller companies and simple use cases
- Pricing is capacity + tier based, so forecasting costs requires understanding expected volumes and job runtimes
- Some advanced capabilities require higher tiers
Pricing model: Tiered subscription + capacity-based
Pricing: Starter / Standard / Premium / Enterprise (typically quote-based)
Reviews:
📝 Gartner Reviews
10. Meltano

Meltano is an open-source ELT framework built around Singer connectors and developer workflows. It’s popular for version-controlled pipelines and CI/CD-driven data engineering. Meltano is best for teams that want full ownership over their ingestion stack.
Pros:
- CLI-first + version-controlled
- Open-source & modular
- Dev-friendly for custom pipelines
- SDK to build Singer taps and targets
Cons:
- Steep learning curve for non-devs
- Requires manual deployment
- Transformations typically done via dbt
- Higher maintenance than managed tools
Pricing model: Free open source + optional paid support/managed
Pricing: Free (self-hosted), custom (managed), paid support packages
All the managerial tasks are handled under the hood, leaving you to focus on getting or consuming the data you need.
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
11. Rivery

Rivery is a managed ELT platform that helps teams load data into a warehouse and transform it post-load. It supports building pipelines via UI and includes scheduling and monitoring features. Rivery is best for teams that want a UI-driven ELT tool with flexible integrations.
Pros:
- Supports custom integrations through native GUI
- Has reverse ETL option
- Supports Python
- Has data transformation capabilities
- Great customer support
Cons:
- Lack of advanced error handling features
- Cannot transform data on the fly (ETL)
- Complex pricing model
- UI is lacking for very complex pipelines
- Documentation can be lacking
Pricing model: Credit-based usage
Pricing: $0.75 per credit (100MB of data replication)
As a data analyst, I find the tool really easy to use; it's intuitive how you connect to the different data sources and create your data pipelines.
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
12. Azure Data Factory

Azure Data Factory (ADF) is Microsoft’s cloud service for building ETL/ELT pipelines in Azure. It includes a drag-and-drop pipeline designer, broad connectivity, and the ability to run transformations via Databricks or stored procedures. ADF is best for teams already committed to the Azure ecosystem.

Pros:
- Scales well in Azure environments
- Rich native connectors
- SSIS support
- Good for hybrid cloud/on-premises
- Strong security and compliance
Cons:
- Complex interface
- Charges per pipeline activity, per DIU for data flows, and for data movement across regions
- Error messages can be vague
- Azure-specific quirks may require specialized knowledge
- UI can be slow on large pipelines
Pricing model: Consumption-based (per activity + compute)
Pricing: Pay per activity run + data movement; starts ~$0.25 per DIU-hour for data flows
Its flexibility in connecting diverse data sources and integration with the Azure ecosystem are standout advantages.
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
13. AWS Glue

AWS Glue is a fully managed, serverless ETL service on AWS. It can generate PySpark ETL jobs, run them on schedules/triggers, and integrate tightly with S3 and other AWS services. AWS Glue is best for AWS-native stacks that want Spark ETL without managing clusters.
Pros:
- Serverless, no infrastructure to manage (Spark under the hood)
- Built-in Data Catalog for schema discovery and integration with Athena
- Supports Python (PySpark) and Scala ETL scripts
- Deep integration with AWS ecosystem (CloudWatch, IAM, S3 triggers)
Cons:
- Costs can be unpredictable for long-running jobs (billed per DPU-hour)
- Debugging PySpark jobs can be cumbersome
- Multi-cloud/on-prem sources require additional setup
Pricing model: Consumption-based (DPU-hour + job costs)
Pricing: $0.44 per DPU-hour (development endpoints) + per-job costs
My team built a framework in AWS Glue to fetch data from multiple platforms and store it in S3 in the format we specified. It streamlined our integration and data collection.
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
14. Skyvia

Skyvia is a cloud platform for ETL, replication, backup, and integration through a browser UI. It supports common SaaS and database sources and can load into warehouses or cloud databases. Skyvia is best for simple no-code ETL and scheduled imports.
Pros:
- Fast, no-code setup for 70+ sources
- Incremental loads and schema auto-detect for many sources
- Built-in replication and backup options
- Free tier available
Cons:
- No advanced transformation engine
- Row/connector-based pricing can be costly at high volume
- Smaller community and support footprint
Pricing model: Freemium + tiered subscription
Pricing: Free (limited); paid plans from $15/month for 10k rows
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
15. Portable.io

Portable.io is a managed ETL service focused on long-tail connectors—niche APIs that other platforms often don’t support. It’s designed for extract-and-load into warehouses with a flat per-connector model. Portable.io is best for teams that need connector breadth with minimal maintenance.
Pros:
- 1,000+ connectors including niche sources
- On-demand custom connector development at no additional cost
- Flat per-connector pricing; no volume-based fees
- Fully managed maintenance (API/schema changes)
- Set-and-forget simplicity
Cons:
- EL-only (no in-platform transformations)
- Cloud-only SaaS (no on-prem option)
- No reverse ETL features
- Limited scheduling granularity out of the box
Pricing model: Per-connector subscription
Pricing: Flat per connector (no volume fees)
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
16. Integrate.io

Integrate.io is a low-code platform for ETL, ELT, and reverse ETL, with a drag-and-drop UI for pipeline design. It supports hybrid deployments using secure agents for on-prem sources. Integrate.io is best for teams that want one tool for ingestion + transformation + activation.
Pros:
- 100+ connectors across analytics and operational destinations
- Visual pipeline builder with transformation expressions
- Hybrid deployments via secure agent
- Unified ETL/ELT + reverse ETL
- Workflow orchestration and scheduling
Cons:
- Cloud-only SaaS (no fully on-prem option)
- UI can feel complex initially
- Debugging less polished than specialized tools
- Pricing can be high for small teams (custom quotes)
- Documentation may lag for newer features
Pricing model: Custom quote (connectors + volume)
Pricing: Custom, based on connectors & volume
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
17. Dataddo

Dataddo is a no-code data integration tool built for business users, offering ETL/ELT, reverse ETL, and dashboard integrations. It handles API changes and pipeline monitoring, and includes caching options. Dataddo is best for teams that want simple setup and low-maintenance pipelines.
Pros:
- No-code setup for non-technical users
- Integrates with 300+ platforms
- Connector requests and onboarding are well-handled
- Competitive pricing for smaller teams
Cons:
- Some users report delays for complex issues
- Niche sources may not be instantly available
- Plan changes/cancellation can be frustrating
Pricing model: Subscription (flow-based)
Pricing: $99 / month for 3 data flows
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
18. dltHub

dlt is an open-source Python library for building code-first ELT pipelines. It handles schema inference, incremental loading, and retries automatically, and runs in any orchestration environment. dlt is best for engineering teams that want lightweight ingestion with strong developer ergonomics.
Pros:
- Open-source and free
- High flexibility via Python code
- 60+ connectors with schema evolution
- Built-in incremental loading and state management
- Works with Airflow, Prefect, cron, etc.
Cons:
- No graphical UI
- Requires engineering to deploy and schedule
- Limited built-in transformations vs ETL suites
- Monitoring/observability must be built externally
- Smaller community vs bigger platforms
Pricing model: Free open source
Pricing: Free (open-source)
Reviews: 📝 Medium Review
19. Rudderstack

RudderStack is a developer-focused customer data platform that routes event data from web/mobile/server sources to warehouses and downstream tools. It supports real-time and batch event processing and is often used in warehouse-first architectures. RudderStack is best for teams that want control and privacy around customer event pipelines.
Pros:
- Developer-focused and flexible
- Reliable event capture + fast warehouse delivery
- Strong SMB/mid-market onboarding
- Supports 200+ destinations
Cons:
- Less intuitive for non-technical users
- Reverse ETL/cohort features can lag specialized vendors
- Docs/alerts need improvement (some report steep onboarding)
Pricing model: Tiered subscription (events-based)
Pricing: Free for 250,000 monthly events; starter $200/month for 1 million events
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
20. Informatica

Informatica is an enterprise data integration platform known for ETL, data quality, and governance at scale. It spans on-prem PowerCenter and cloud-native IDMC for hybrid environments. Informatica is best for large organizations that need end-to-end enterprise data management.

Pros:
- Enterprise-grade capabilities
- Strong data quality features
- Cloud integration; scalable
- 1,200+ connectors
Cons:
- Expensive for SMB/mid-market
- Specialized skills required
- Infrastructure/setup can be heavy
Pricing model: Enterprise licensing + subscription (custom quotes)
Pricing: PowerCenter enterprise licensing; Cloud subscription (custom quotes)
Reviews: 📝 Gartner reviews
21. CloverDx

CloverDX is an enterprise ETL/ELT platform built for complex workflows with both code and GUI development. It’s often used for transformation-heavy integration, data migration, and automation. CloverDX is best for teams that need flexible design plus enterprise-grade control.
Pros:
- Metadata-driven schema handling and impact analysis
- Visual flow designer with reusable components
- Supports batch + streaming ingestion across many systems
- Built-in scheduling, monitoring, alerting, RBAC
Cons:
- Higher licensing costs
- Designer can feel heavy for simple tasks
- Smaller community vs open-source
Pricing model: Subscription/perpetual (custom quote)
Pricing: Subscription or perpetual licensing (custom quotes, typically $20k+ annually)
"Ability to design elegant data flows and work with really dirty data. The visual design ensures that you write proper rules to deal with a variety of data quality issues."
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
22. Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)

SSIS is Microsoft’s enterprise ETL tool for batch workflows like data warehouse loads, file transfers, and cleansing. It’s primarily on-prem with SQL Server, but can run in Azure via Data Factory. SSIS is best for Microsoft-centric environments with established SQL Server pipelines.
Pros:
- Strong fit for SQL Server/Azure/Power BI stacks
- Robust transformation and control-flow tooling
- Extensible with C# / VB.NET
- Logging and recovery features
Cons:
- Limited native connectors vs modern SaaS tools
- Windows-centric and less cloud-native
- Visual Studio GUI can be unintuitive for new users
- Batch-first; not real-time native
Pricing model: Licensing + Azure compute (varies by deployment)
Pricing: Pricing based on VM size + licensing model (pay-as-you-go or Azure Hybrid Benefit)
Reviews: 📝 Trustradius reviews
24. IBM InfoSphere DataStage

IBM DataStage is an enterprise ETL platform built for high-performance batch processing and massive data volumes. It supports parallel processing, rich transformation libraries, and governance features via the InfoSphere ecosystem. DataStage is best for large enterprises with complex environments and heavy throughput needs.
Pros:
- Parallel processing engine for large data volumes
- Metadata, lineage, and governance integration
- On-prem and cloud/container deployment options
- Extensive transformation library
Cons:
- Limited modern SaaS coverage vs newer tools
- High enterprise cost
- Complex setup and ramp-up
- Requires specialized expertise for best performance
Pricing model: Enterprise licensing (custom quote)
Pricing: Usually six-figure annual
Reviews: 📝 G2 reviews
25. Oracle Data Integrator (ODI)

Oracle Data Integrator is an ELT platform that pushes transformations down to the target database for performance at scale. It supports on-prem, cloud, and hybrid deployments and is commonly used in Oracle-centric environments. ODI is best for enterprises that want ELT efficiency inside Oracle-heavy stacks.
Pros:
- Broad source/target support (Oracle and non-Oracle)
- Reusable Knowledge Modules simplify development
- Robust monitoring and error handling
Cons:
- Best fit in Oracle ecosystems; non-Oracle setups can require extra config
- Licensing/implementation can be a barrier for smaller orgs
- Batch-oriented; not built primarily for real-time
Pricing model: License-based (processor/user)
Pricing: Roughly $30,000 per processor or $900 per user (plus support)
Reviews: 📝 G2 reviews
26. SAP Data Services

SAP Data Services is an enterprise ETL and data quality platform used for integration, migration, and transformation-heavy workflows in SAP environments. It typically runs on-prem or in private cloud/IaaS setups. SAP Data Services is best for organizations deeply invested in SAP systems.
Pros:
- Strong SAP ecosystem integration
- Scales to large volumes
- Useful for migration/integration in SAP estates
Cons:
- Licensing and implementation can be expensive
- Extensibility can be limited in non-SAP-heavy environments
Pricing model: Enterprise licensing (varies)
Pricing: Varies by deployment; typically quote-based
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
27. Google Cloud Data Fusion

Cloud Data Fusion is Google’s managed no-code/low-code service for building ETL/ELT pipelines through a visual interface. It integrates with BigQuery and other GCP services and supports reusable components. Data Fusion is best for teams building primarily on Google Cloud who want a managed visual pipeline tool.
Pros:
- Team collaboration + centralized pipeline management
- Scales for batch and real-time patterns
- Tight GCP integration (BigQuery, GCS, Pub/Sub)
- Usage-based pricing
Cons:
- Plugin/connectors can limit deep customization
- Complex transformations can be challenging initially
- Pricing can increase at scale
Pricing model: Usage-based (instance + Dataproc execution)
Pricing: Dev costs from $0.35 to $4.20/hr + Dataproc charges
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
28. Stitch

Stitch is a lightweight ELT tool that extracts data from sources and loads it into a warehouse. It has historically been tied to the Singer ecosystem and is often used for straightforward ingestion needs. Stitch is best for simpler pipelines where you want quick setup without a big platform.
Pros:
- Built on Singer ecosystem (broad tap/target availability)
- Encrypted logs for troubleshooting
- Fits well inside the Qlik ecosystem
Cons:
- Smaller native catalog than many modern platforms
- Pricing can jump across tiers
- Volume limits can be restrictive at scale
Pricing model: Subscription (rows-based tiers)
Pricing: $100 / 5M rows
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
29. Qlik Replicate

Qlik Replicate is a data replication and ingestion tool focused on moving data between databases, warehouses, and big data platforms. It supports snapshots and incremental replication and is known for log-based CDC with low source impact. Qlik Replicate is best when you need replication/CDC and plan to do transformations elsewhere.
Pros:
- High-performance CDC with minimal source impact
- Automated schema change handling
- GUI-based configuration and monitoring
- Cloud-native or on-prem deployments
Cons:
- No built-in transformations (replication-only)
- Enterprise pricing can be high at scale
- Learning curve for advanced replication scenarios
Pricing model: Subscription/perpetual (custom quote)
Pricing: Custom quotes; can be six-figure enterprise costs
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
30. Striim

Striim is a real-time data integration and streaming platform built for low-latency pipelines using Change Data Capture. It’s widely used for enterprise streaming and strong Oracle support, competing with tools like Debezium and Estuary. Striim is best for environments that need streaming-grade ingestion plus operational analytics.
Pros:
- Designed for large-scale real-time replication
- Combines stream processing and data integration
- Supports incremental batch replication and scheduled snapshots
Cons:
- Stream-processing model can be harder to learn than typical ETL tools
- Uses Tungsten Query Language (TQL), less approachable than SQL
- Complex CDC may require custom scripting
Pricing model: Custom quote
Pricing: Custom pricing
Reviews: 📝 G2 Reviews
31. Apache Kafka

Apache Kafka is an open-source event streaming platform for high-throughput, low-latency pipelines and real-time processing. It’s commonly paired with ETL/ELT tools to transport event data into warehouses, lakes, and operational systems. Kafka is best as streaming infrastructure, not as a standalone ETL tool.
Pros:
- Widely used for real-time analytics, monitoring, and event streaming
- Horizontally scalable for large workloads
- Replication improves reliability and fault tolerance
Cons:
- Requires significant operational expertise
- Distributed architecture increases management effort
- Needs Kafka Connect or custom code for ETL/ELT workflows
Pricing model: Free open source
Pricing: Free to use
Reviews: 📝 Trustradius reviews
32. Debezium

Debezium is an open-source change data capture (CDC) tool that streams row-level database changes into Kafka. It reads transaction logs and emits change events so downstream systems can react quickly. Debezium is best for teams that want CDC into Kafka and can operate the surrounding infrastructure.
Pros:
- Built on Kafka Connect (great for Kafka-native stacks)
- Incremental snapshot patterns for large tables
- Reliable change capture for supported databases
Cons:
- Requires Kafka + Kafka Connect operational ownership
- Primarily CDC-to-Kafka (broader ETL needs extra tooling)
- Backfills/replay often require custom workflows
Pricing model: Free open source
Pricing: Free to use
Reviews: 📝 Medium review
33. SnapLogic

SnapLogic is an iPaaS platform for ETL, ELT, and application integration using a visual “Snap” architecture. It includes a large connector library and AI-driven pipeline assistance. SnapLogic is best for organizations that want one integration platform spanning data + apps.
Pros:
- 500+ Snap connectors across SaaS, databases, and on-prem sources
- Visual pipeline designer with AI-driven suggestions (Iris)
- Managed execution with autoscaling and multi-cloud support
- Supports batch and real-time patterns
Cons:
- Premium pricing can be cost-prohibitive for SMBs
- Designer can feel cluttered for large pipelines
- Mostly SaaS-based; limited self-hosted options
Pricing model: Subscription (connector + usage-based)
Pricing: Subscription; starts ~$50k/year (as written in your draft)
"Overall I was able to create pipelines required easily to migrate and fill data manually, which helped me a lot and improved my performance."
Reviews: 📝 Gartner Reviews
34. Singer

Singer is an open-source standard for building composable ETL pipelines using taps (extract) and targets (load). Components communicate via JSON over stdin/stdout, making pipelines modular. Singer is best for developers who want lightweight building blocks and don’t need a managed UI.
Pros:
- Large ecosystem of taps and targets
- Easy to extend with custom taps/targets
- Strong community history and continued usage
Cons:
- Requires technical setup and maintenance
- Less automation than modern managed tools
- Connector quality varies across the ecosystem
Pricing model: Free open source
Pricing: Free to use
Reviews: 📝 Stackshare reviews
35. Databricks Lakeflow

Databricks Lakeflow provides a managed environment for building data pipelines and lakehouse workflows on Databricks. It combines storage, compute, and orchestration to simplify ETL/ELT inside the Databricks ecosystem.
Pros:
- Tight integration with Databricks compute and Delta Lake
- Good for data engineering teams already standardizing on Databricks
- Scales with Databricks clusters and SQL workloads
Cons:
- Best value only inside Databricks-heavy stacks
- Pricing depends on Databricks usage (can be expensive)
Pricing model: Usage-based (Databricks compute + storage)
Reviews: Databricks product and announcement pages
36. IBM StreamSets

IBM StreamSets is a data integration platform focused on streaming and hybrid ingestion patterns. It provides visual pipeline design for both batch and streaming use-cases and integrates with common enterprise data platforms.
Pros:
- Designed for hybrid streaming and batch ingestion
- Visual pipelines with enterprise governance
- Integrates with Kafka, cloud messaging, and enterprise data stores
Cons:
- Enterprise pricing and complexity
- Smaller community than open-source streaming stacks
Pricing model: Quote / enterprise
Reviews: IBM product pages
37. Apache NiFi

Apache NiFi is an open-source flow-based data ingestion tool that makes it easy to route, transform, and mediate data between systems. It’s well suited for edge-to-core ingestion, IoT, and heterogeneous enterprise sources.
Pros:
- Visual flow-based editor for building pipelines
- Fine-grained control over routing, throttling, and provenance
- Good for heterogeneous and edge ingestion use-cases
Cons:
- Operational overhead for large clusters
- Not optimized for in-warehouse transformations
Pricing model: Free open source
Reviews: Apache NiFi project page
38. Apache Hop
Apache Hop is an open-source data orchestration and ETL platform designed for metadata-driven pipeline development. It’s a modern alternative to legacy ETL designers with a focus on reusability and developer ergonomics.
Pros:
- Open-source with a growing set of plugins and community tools
- Visual pipeline design with reusable components
- Good for teams wanting a GUI-driven, open ETL tool
Cons:
- Maturity and ecosystem smaller than long-established tools
- Requires engineering to operate at scale
Pricing model: Free open source
Reviews: Apache Hop project page
39. Matia
Matia is a cloud ELT platform focused on extracting data from SaaS sources into analytics warehouses. It emphasizes simplicity and quick setup for analytics teams that need ingested data without heavy engineering overhead.
Pros:
- Fast setup for common SaaS sources
- Focused on analytics-ready ingestion and simple scheduling
- Managed service with support for common warehouses
Cons:
- Smaller connector catalogue than larger players
- Limited advanced transformation capabilities in-platform
Pricing model: Subscription / tiered
"Matia unifies ETL, observability, catalog, and reverse ETL so teams can focus on driving actionable insights and accelerating innovation."
Reviews: Matia product pages
40. Xplenty

Xplenty is a cloud-based ETL/ELT platform offering a visual pipeline designer and pre-built connectors. It targets teams that want a low-code way to extract, transform, and load data into warehouses without heavy engineering.
Pros:
- Visual pipeline builder with ready-made transformations
- Good connector coverage for common SaaS and DB sources
- Simple deployment and scheduling
Cons:
- Pricing can be higher for heavy usage
- Not as feature-rich for large enterprise governance scenarios
Pricing model: Subscription
Reviews: Xplenty product pages
ETL FAQs: Common Questions Answered
What’s the difference between managed vs self-hosted ETL tools?
Below is a comparison table highlighting the key differences between managed ETL tools and open-source (self-hosted) ETL tools:
| Feature | Managed | Open-source (self-hosted) |
|---|---|---|
| Runs on | The vendor’s servers | Your own servers |
| Managed by | The vendor | Your team |
| Data control | Data goes through the vendor’s systems (usually encrypted) | Data stays entirely within your infrastructure |
| Setup | Fast, web-based | You install and configure it manually |
| Cost | Subscription | May be free (if open source), but you pay for infrastructure and staff |
| Compliance | Handled by vendor (SOC 2, GDPR, etc.) | You must ensure compliance yourself |
What are the main use cases for an ETL pipeline?
- Data Migration: Moving data between systems, especially during system upgrades or replacements.
- Data Warehousing: Consolidating data from multiple sources into a central repository for analysis and reporting.
- Data Integration: Combining data from different sources to provide a unified view.
- Data Transformation: Cleaning, enriching, and transforming data to meet business needs.
- Automating manual workflows: Reducing human error and saving time by automating repetitive data tasks.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) transforms data before loading it. ELT loads raw data into the warehouse first, then transforms it. ELT is more common with modern cloud data stacks.
Is open-source better than managed ETL tools?
It depends on your team. Open-source (like Airbyte or Meltano) offers control and flexibility but needs engineering time. Managed tools (like Weld or Fivetran) offer speed and simplicity.
Which tool is best for streaming data or CDC?
Estuary is a strong CDC/streaming-first option. For CDC-heavy replication, Qlik Replicate is widely used, and Debezium is a popular open-source choice (typically used with Kafka).
How do I know which type of pricing fits me the best?
Finding the best pricing model for your needs can be challenging and is based on many factors, such as the volume of your data, syncing frequency, budget or monthly active rows.