Connecting data, tables, and creating a model
Before you start writing your first queries in SQL, you need to prepare a little bit.
- It’s a good idea to create an account with Weld, or request access if your organization already has a Weld account.
- Once you have a Weld account, you can connect the sample data to your data warehouse, as we’ll be using this data set in the tutorial.
If you’re new to Weld:
- If you’ve just signed up for Weld, the e-commerce sample data will be suggested for you to connect to.
- If you already had an account in Weld, you might need to set up a new gather sync through this connector. You’ll find this in the Data Source section inside Weld.
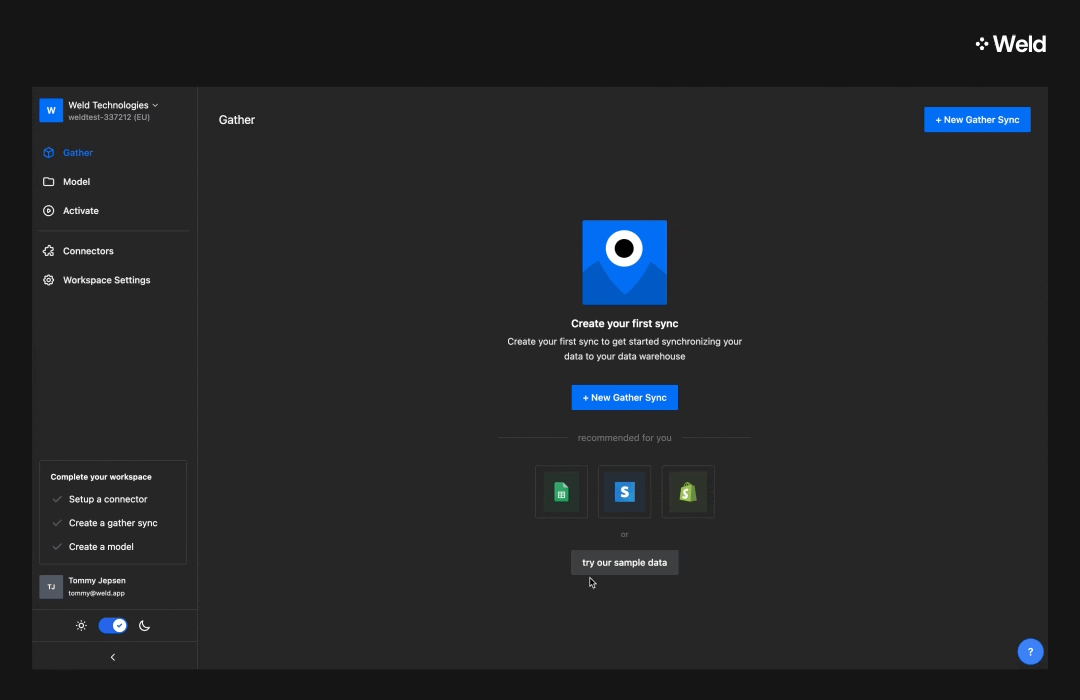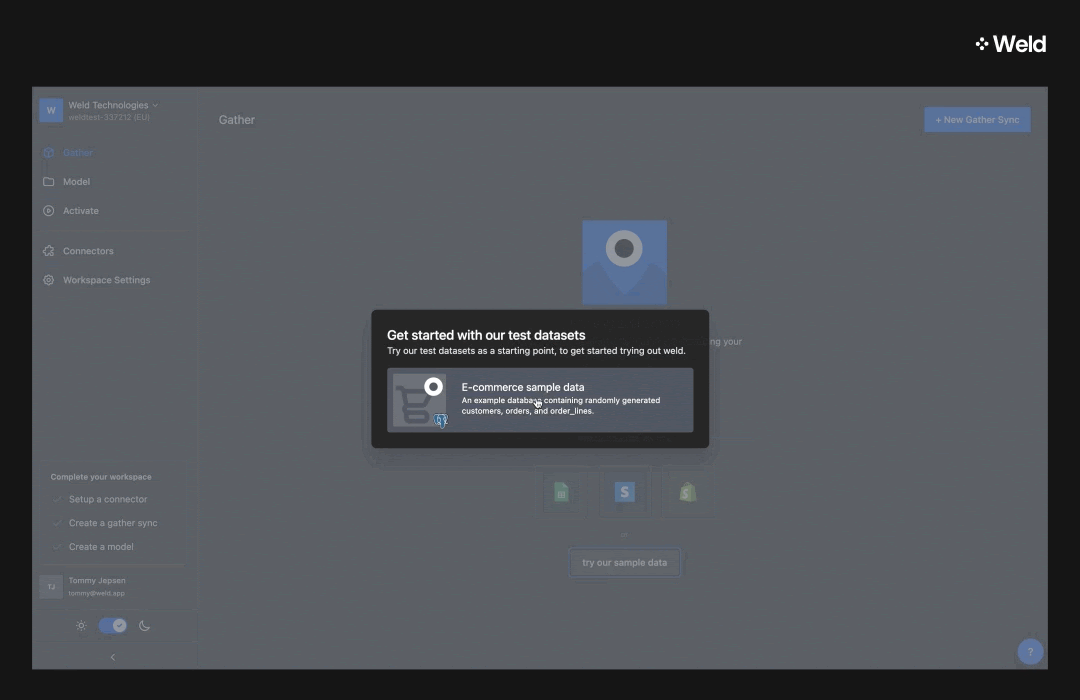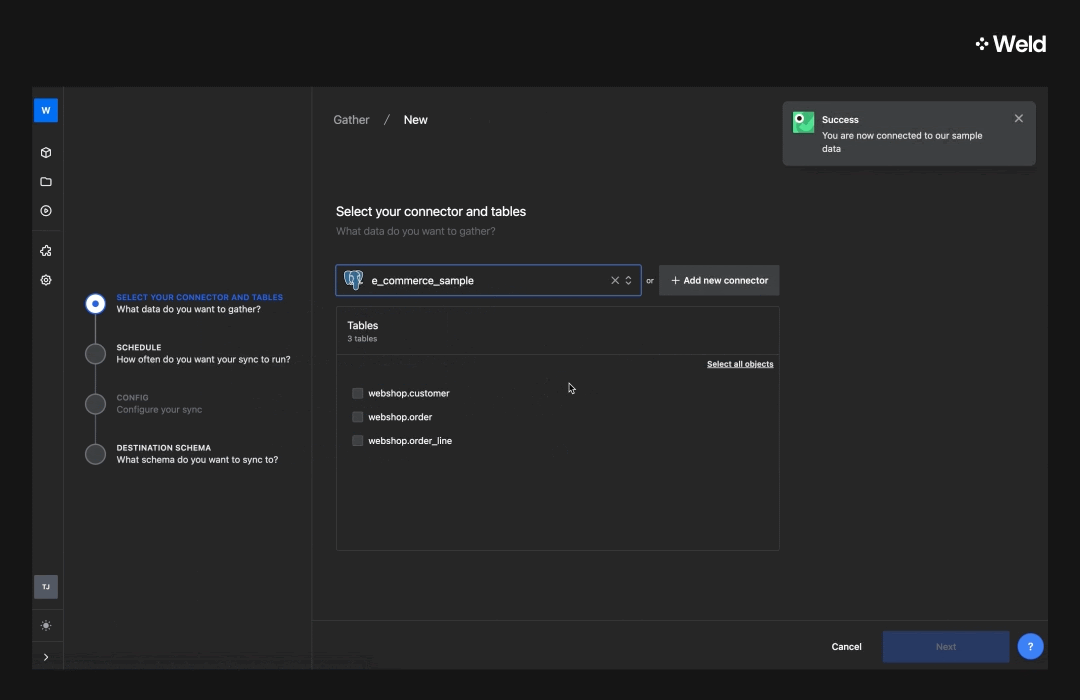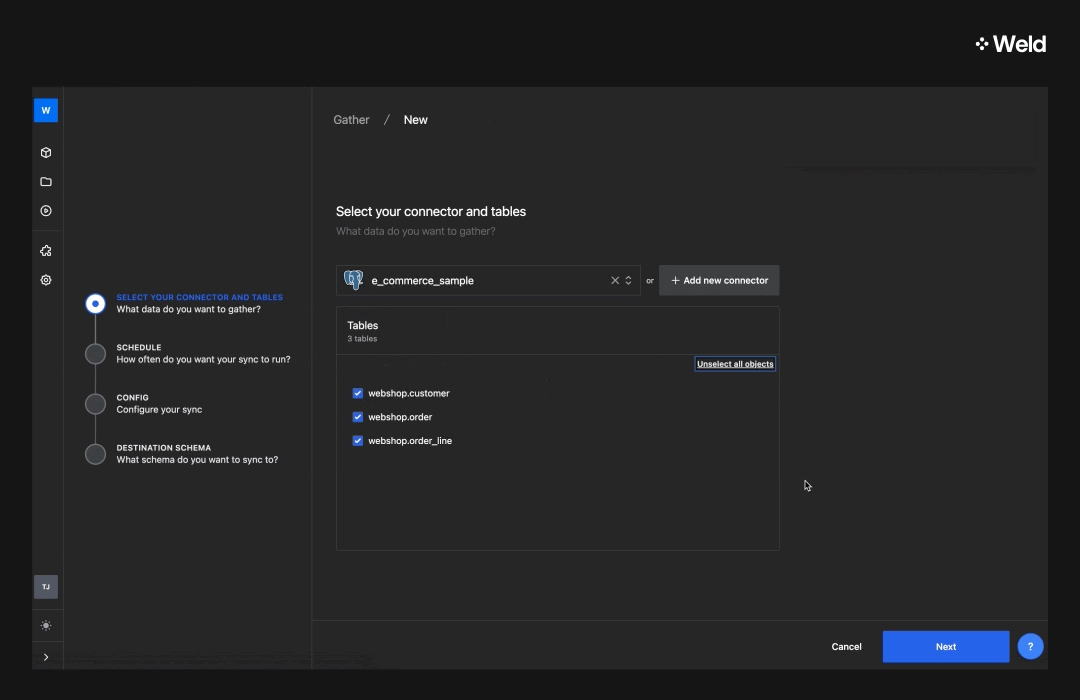
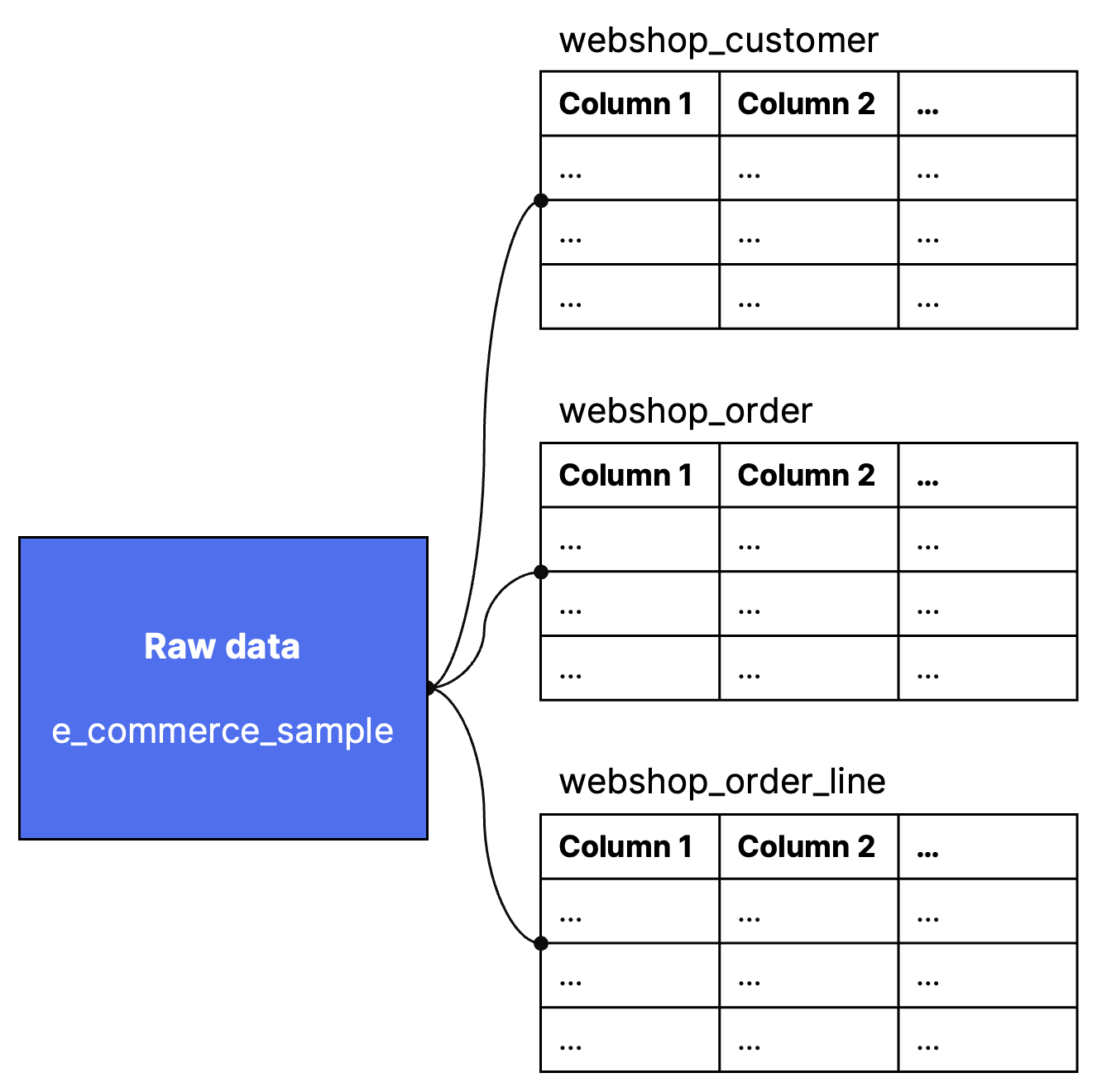
Once you’ve connected to a data source, you’ll get access to the data. This will typically consist of several tables, each with different pieces of information. You can see the different tables once you set up the connector, or in the sidebar to the left in the Weld Editor in the Raw Data section. As you can see, the sample e-commerce data set consists of three different tables:
- Webshop customer (with one row of information for each customer in the webshop),
- Webshop order (one row for each order in the shop), and
- Order line (one row for each line in the orders)
If you connect to other tools such as Hubspot or Stripe, these will also consist of several different tables representing the different information available in these tools.
Create your first model
Now that you’ve connected the data for this Getting Started guide, the final step before diving into SQL is to create a model.
A model is a file where you define how you’d like to manipulate the raw data to get the results you require.
How to create a model:
- In the left sidebar, click on Model to go to the model layer.
- Click ‘+ New’ to create a new model.
That’s it — you’ve now created your first model!
It doesn’t matter where you save it or whether it’s published or not at this stage.
Important Notes Before You Start Writing SQL
- Your raw data is never changed. When you write SQL in Weld, you’re creating a layer on top of the data — not altering the original data itself.
- Models are isolated. Adding or editing your model won’t affect data in dashboards or models created by others. (e.g. in any dashboards someone in your organization has set up) To change shared data, you would have to enter their models and make changes to them, and publish those changes. You can therefore safely create as many new models as you want in Weld, without putting your existing data operations at risk.
- You can reference other models. You can reference not only different sources of raw data, but also other data models when they’re made public. This means you can split your analysis into several steps in different models before you arrive at the end result you’re looking for and want to add to a dashboard or activate by sending the data back to your business tools.
